AIM — Free & Open
CC BY-NC-SAAIM is free and open for non-commercial reuse. Try a free AIM pilot (CSV + memo) — support is optional and helps sustain translations, research, and free access.
Table of Contents
Introduction: A Mental Crisis or a Bridge to New Understanding
“Evolution is killing me.” With these poignant words, one young person expressed the inner turmoil between his faith in God and the scientific evidence for evolution. 1 This struggle is not uncommon. Many Muslims find themselves in a difficult position, caught between what appears to be a contradiction between Islam and Evolution, religious texts and modern scientific knowledge. Must we choose between our minds and our hearts? Does science inevitably lead to atheism, or is there a path to reconciliation? 2
This article is not designed to provide a final answer but to serve as an intellectual guide for readers who are new to the topic. Our goal is to build a bridge of understanding, relying on the latest scientific insights and diverse theological perspectives. The true dialogue is not a conflict between “science and the Quran,” but a discussion between evolving human hypotheses and divine revelation that offers us timeless guidance and dignity.
1. Evolution: From “Hunch” to “Scientific Fact”
One of the greatest sources of misunderstanding is the confusion between the everyday meaning of the word “theory” and its meaning in a scientific context.
- Theory in everyday use: Refers to a mere idea, hunch, or unproven speculation.
- Theory in a scientific context: A comprehensive, well-substantiated explanation of a natural phenomenon, supported by a vast body of evidence from fields as diverse as molecular biology, paleontology, comparative anatomy, and genetics.
Based on this definition, the scientific community considers evolution to be both a fact and a theory. The “fact” of evolution is that the process of biological change has occurred and continues to occur. The “theory” of evolution is the explanatory framework that explains “how” this change happened through mechanisms like natural selection, mutation, and genetic drift.
The common distinction between “microevolution” and “macroevolution” is also a source of confusion. Microevolution refers to small-scale changes within a single species (like bacterial resistance to antibiotics), while macroevolution refers to large-scale changes that lead to the emergence of new species. Scientists assert that both levels rely on the same established mechanisms, and the difference between them is one of scale, not of mechanism or certainty. 3
2. Scientific Evidence: Answers to Common Questions
Between Islam and Evolution, While it may seem that the theory of evolution faces significant scientific challenges, most of the criticisms raised in public discourse have already been addressed by scientists. Understanding the available scientific evidence allows us to place the debate in its proper context. 4
The Fossil Record: Life’s Story in Stone
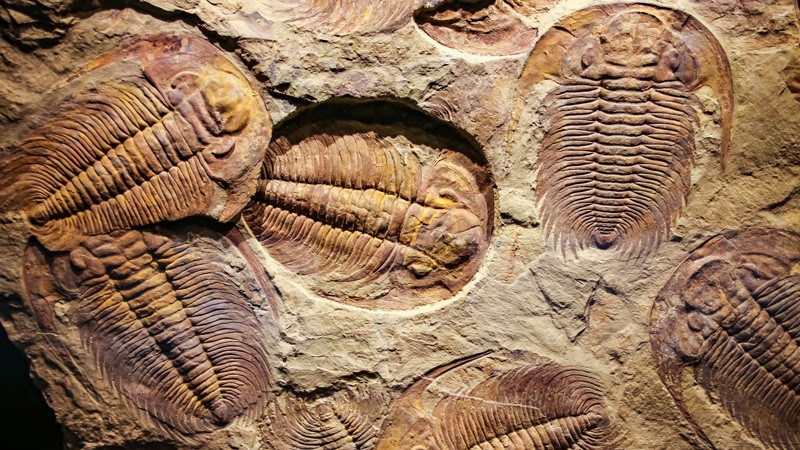

It was once claimed that the fossil record suffered from major “gaps” that failed to support gradual transitions between species. This is an outdated argument. While the fossil record is inherently incomplete—as only a tiny fraction of ancient organisms are ever preserved as fossils—it is rich with transitional fossils that clearly illustrate the links between different groups of living things. 5
Some prominent examples include:
- Tiktaalik: A 375-million-year-old fossil that represents a transitional link between fish and four-limbed vertebrates. 6
- Ambulocetus natans: A fossil of an amphibious mammal that lived about 49 million years ago, considered a transitional phase between land mammals and whales. 7
The existence of these fossils refutes the idea of fundamental gaps and affirms that the fossil record provides strong evidence for evolutionary transitions.
Irreducible Complexity: A Rejected Concept
Between Islam and Evolution, The concept of “irreducible complexity” is a central argument used by opponents of evolution, particularly within the Intelligent Design movement, which the scientific community considers pseudoscience. 8 This argument claims that certain biological systems, such as the bacterial flagellum, are so complex that they would cease to function if a single part were removed, thus making their gradual evolution impossible.
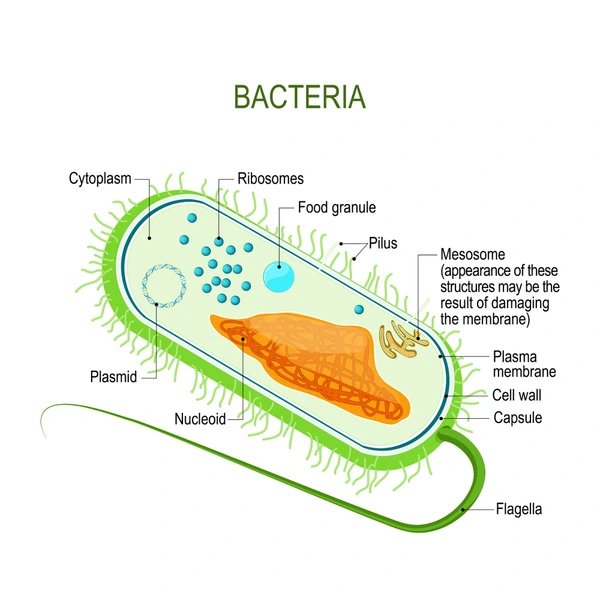
However, this claim has been decisively refuted by the scientific community. Research has shown that the basal body of the bacterial flagellum shares core components with the “Type III secretion system” (TTSS), a simpler, functional system found in some bacteria. 9 This similarity demonstrates how a complex system can evolve from simpler components that once served a different function, proving that evolution does not rely solely on improving existing functions but can co-opt parts from other systems to create new ones.
The Appendix: Function Does Not Negate Origin
Between Islam and Evolution, The human appendix was once considered a classic example of a “vestigial organ” that had lost its original function. However, recent research has revealed that it plays a vital role in the immune system and serves as a “safe house” for beneficial gut bacteria, helping to replenish them after illnesses. 10
While some might use this discovery to argue that the appendix is not evidence for evolution, this conclusion is flawed. Between Islam and Evolution, The presence of a current function does not negate an organ’s evolutionary history. 11 In fact, the independent evolution of the appendix in different mammalian species, such as rodents and primates, provides additional evidence that it offers a selective advantage, thereby supporting the evolutionary framework. The discovery of its new function enriches our understanding of the complexity of evolution; it does not disprove it.
3. Adam’s Origins in the Quran and Sunnah: The Case for an Exceptional Creation
Between Islam and Evolution, The position held by most mainstream Muslim scholars is that the creation of Adam was a unique and direct event. This belief is not merely a personal opinion but a foundational tenet of Islamic faith, supported by clear evidence from the Quran and Sunnah.

- Direct Creation from Clay: The Quran asserts that God created Adam from dust or clay, a direct process distinct from typical human procreation. The Quran states: {Indeed, the example of Jesus to Allah is like that of Adam. He created him from dust; then He said to him, “Be,” and he was.} 12 This verse explicitly compares Adam’s creation to the miraculous birth of Jesus, emphasizing its extraordinary and non-biological nature.
- The Infusion of the Soul: The Quran emphasizes that what distinguishes humanity is the soul infused into Adam by God. {And when I have proportioned him and breathed into him of My [created] soul, then fall down to him in prostration.} 13 This divine act of breathing the soul gives humanity a special dignity and a unique status in creation.
- Textual Silence on Human Evolution: Proponents of this view argue that the Quran and Sunnah do not contain any references to a gradual human evolution from a lesser species. On the contrary, the texts are explicit that all humans are direct descendants of Adam and Eve. 14
- The Scope of Science vs. Revelation: For scholars who hold this view, science can explain the evolution of other living things, but it cannot account for the direct creation of Adam. This highlights a boundary for science, which is concerned with the natural world, while the realm of the unseen and miraculous remains the domain of revelation and faith. 15
This evidence forms a solid basis for the “Human-Exception Creationism” view, which is widely accepted among Muslims: that evolution may explain the diversity of life on Earth, but the creation of the first human was a unique event, independent of that biological process.
4. The Intellectual Diversity in Islamic Thought
Between Islam and Evolution, The debate over evolution is not new to Islamic intellectual history. Ancient and modern Muslim scholars have offered a spectrum of views, demonstrating that the discussion is a continuous, dynamic process.
- Literal Creationism: This view rejects evolution entirely and holds that all species were created in their current form, with a direct creation for Adam. This is the predominant view among mainstream scholars in the post-colonial Muslim world.
- Theistic Evolution: This position sees evolution as the process willed and guided by God to create all forms of life, including humans. Proponents argue that Quranic verses describing creation from water or clay in “stages” (Quran 71:13-14) can be interpreted as metaphors for a gradual, organic process directed by God.
- Historical Voices:
- Al-Jahiz (9th Century): Observed what can be seen as an early reference to the “struggle for existence” and “food chains,” noting how environmental factors influence organisms to develop new traits. 16
- Ibn Khaldun (14th Century): Wrote in his Muqaddimah about a natural hierarchy from minerals to plants, animals, and finally humans. He even suggested that humans evolved from “the world of the monkeys,” highlighting the human capacity for reason as the key distinguishing factor. 17
These views show that the dialogue between science and religion in Islam is not a modern invention but has deep historical roots.
5. Ethical and Social Implications: Beyond Biological Science
Between Islam and Evolution, One of the greatest fears about accepting evolution is that it might lead to a loss of human dignity and a breakdown of social morality. Some mistakenly believe that “survival of the fittest” is an ethical principle to be applied to human society.
However, this is a profound misunderstanding.
- Science Doesn’t Dictate Morality: Science describes “how” things work in the natural world, but it cannot tell us “what” we ought to do. Morality cannot be derived from scientific theory alone.
- Morality Transcends Nature: Thomas Henry Huxley, a prominent proponent of Darwin, strongly opposed applying the principles of biological evolution to human society. He argued that human ethics often contradict natural processes. While competition may be beneficial for survival in nature, cooperation and compassion are the foundations of human society. 18
- Morality in Islam: For Muslims, the source of ethics and social responsibility is divine revelation. Human dignity is not dependent on our physical form but on the soul God breathed into us. Humans are endowed with intellect and the capacity to choose between right and wrong, a quality not found in other beings. Islam places the responsibility on humanity to work for social progress within the framework of its moral and ethical code.
Conclusion: Science Reveals, Faith Gives Meaning
Between Islam and Evolution, The crisis of faith that many face regarding evolution is an opportunity to re-examine the relationship between science and religion. There is no inherent conflict between science, which describes “how” the world works, and faith, which provides answers to the ultimate question of “why.”
The challenge is not to deny science but to develop our understanding of sacred texts in a way that aligns with the truths revealed to us by God in the natural world. Accepting evolution as a biological mechanism does not diminish God’s greatness; it enhances it by revealing the incredible wisdom of a Creator who designed a system that continues to change and adapt.
Ultimately, the more we learn about the mysteries of the universe, the more awe we feel before the Creator who perfected everything He created. Between Islam and Evolution, This dialogue is a call for intellectual openness and the belief that intellect and revelation, science and faith, are not in opposition but are two complementary forces that lead humanity to a deeper understanding of the world and our purpose within it.
References
- creationism vs evolution is killing me. ↩︎
- Islam and Evolution: A Religious Perspective on the Theory of Evolution. ↩︎
- Evolution at different scales: micro to macro. ↩︎
- The Quran and Biological Evolution: Towards a Theistic Evolutionary Model. ↩︎
- Taxonomy, Transitional Forms, and the Fossil Record. ↩︎
- Transitional fossil. ↩︎
- Transitional fossil. ↩︎
- Irreducible complexity. ↩︎
- Irreducible complexity. ↩︎
- The functional landscape of the appendix microbiome under conditions of health and disease. ↩︎
- The functional landscape of the appendix microbiome under conditions of health and disease. ↩︎
- The Noble Quran. ↩︎
- Islamic views on evolution. ↩︎
- Islamic views on evolution. ↩︎
- Islamic views on evolution. ↩︎
- Islamic views on evolution. ↩︎
- Islamic views on evolution. ↩︎
- T. H. Huxley’s Evolution and Ethics: Struggle for Survival and Society. ↩︎
Discover more from Ahmed Alshamsy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







